SHOULDER PAIN AND REGENERATIVE MEDICINE
💪 Regenerative Medicine for Shoulder Pain: How Stem Cells Are Changing the Game
🩺 Shoulder Pain: A Growing Concern
Shoulder pain is one of the most common musculoskeletal problems worldwide. It affects athletes, active adults, and older patients alike — often due to tendon injuries, rotator cuff tears, bursitis, or osteoarthritis.
Traditional treatments like painkillers, corticosteroid injections, or physiotherapy may temporarily relieve symptoms but often don’t address the underlying tissue damage.
Regenerative medicine — and specifically stem cell therapy — offers a new therapeutic option aimed at healing damaged tissues, reducing inflammation, and restoring mobility.
- Anatomical illustration of the shoulder joint with common injury zones (rotator cuff, bursa, cartilage).
🧬 What Is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells capable of becoming specialized cells such as tendon, ligament, cartilage, or muscle.
In shoulder injuries, they work through:
- Anti-inflammatory effect — calming chronic irritation and swelling.
- Paracrine signaling — releasing growth factors and cytokines to stimulate healing.
- Regeneration — supporting tendon and cartilage repair.
- Pain modulation — improving the joint environment for lasting relief.
🧠 Think of stem cells as both the “repair crew” and “signal amplifiers” of your body’s healing system.
⚠️ Common Shoulder Conditions Suitable for Stem Cell Therapy
| Shoulder Condition | Typical Symptoms | How Stem Cells Help |
| Rotator cuff tear / tendinopathy | Pain with lifting, weakness, night pain | Stimulate tendon healing, reduce inflammation, promote collagen regeneration |
| Shoulder osteoarthritis | Stiffness, crepitus, pain at rest or activity | Regenerate cartilage, lubricate joint, reduce inflammation |
| Bursitis / impingement | Pain with overhead activity, limited ROM | Decrease inflammation, restore smooth motion |
| Labral injuries / instability | Pain with movement, clicking, weakness | Promote labral healing and joint stabilization |
| Post-operative or sports injury recovery | Pain, weakness, delayed healing | Accelerate tissue recovery and improve healing environment |

- Clinical diagram or MRI illustration of rotator cuff tear.
🩻 How the Procedure Works
- Diagnosis & Planning
Clinical evaluation and imaging (ultrasound, MRI) identify the source and severity of shoulder injury.
- Cell Preparation
Stem cells are obtained either from the patient’s bone marrow or adipose tissue, or prepared from umbilical cord MSCs(allogenic).
- Ultrasound-Guided Injection
The prepared stem cells are precisely injected into the injured tendon or joint space under real-time imaging.
- Recovery & Remodeling
Cells reduce inflammation and promote biological repair over the next weeks to months, without hospital stay or long downtime.
- Clinical photo or diagram showing ultrasound-guided injection into the rotator cuff tendon.
- ALT text: “Ultrasound-guided stem cell injection into the shoulder.”
🌱 Types of Stem Cells Used
| Source | Description | Advantages |
| Bone marrow MSCs | Harvested from iliac crest | Autologous, good tendon healing capacity |
| Adipose-derived MSCs | Taken from abdominal fat | Abundant, minimally invasive |
| Umbilical cord MSCs | Allogenic donor source | Off-the-shelf, high potency, no harvest needed |
| PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) | Platelet concentrate (not stem cells) | Often combined with MSCs to boost effect |
Umbilical cord MSCs are increasingly used because they offer high regenerative power with no donor site morbidity.
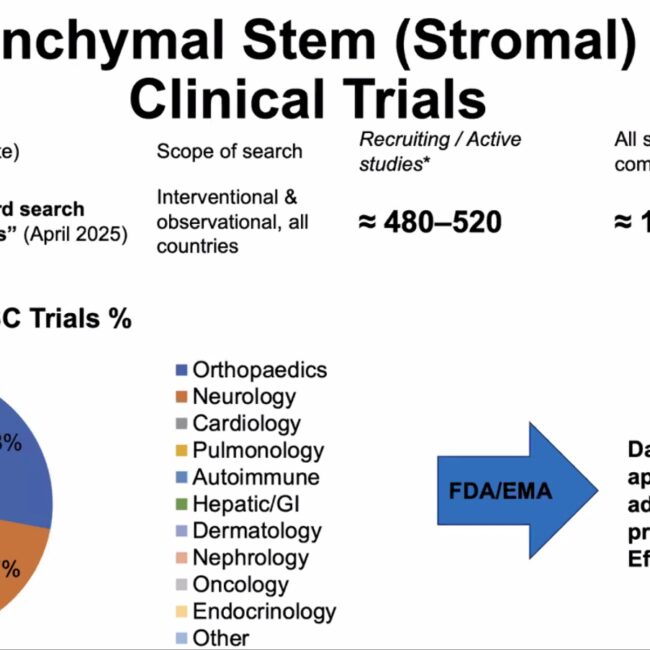
🧪 Scientific Evidence
Several studies support the efficacy of stem cell therapy for shoulder conditions:
- Jo et al., 2018 – Intratendinous injection of adipose-derived MSCs improved pain and function in rotator cuff disease.
- Hurd et al., 2020 – Autologous adipose-derived regenerative cells showed safety and effectiveness in partial rotator cuff tears.
- Caplan, 2017 – Defined the paracrine effect of MSCs as the cornerstone of their therapeutic benefit.
Reported benefits:
- ✅ Significant pain reduction (VAS score)
- ✅ Improved strength and mobility
- ✅ MRI evidence of tendon healing or reduced defect size
- ✅ Fewer complications compared to surgery
- MRI before/after showing tendon healing post MSC injection.
🆚 Stem Cell Therapy vs Conventional Treatments
| Conventional Treatment | Stem Cell Therapy |
| Painkillers or corticosteroids | Treat symptoms only |
| Physiotherapy | Improves function but may not heal structural damage |
| Surgery (arthroscopy, tendon repair) | Effective but invasive, longer recovery |
| Stem Cell Therapy | Minimally invasive, biological healing, faster recovery |
🏃♂️ For many patients, stem cell therapy can delay or avoid surgery, especially in partial tendon tears or early degenerative changes.
👨⚕️ Ideal Candidates for Shoulder Stem Cell Therapy
- Patients with partial or degenerative rotator cuff tears
- Individuals with early shoulder osteoarthritis
- Patients with persistent shoulder pain not responding to conservative treatment
- Athletes or active individuals seeking faster recovery
- Patients who want to avoid surgery
⚠️ Patients with massive tendon ruptures or advanced OA may still need surgical options.
🧭 Recovery and Results
- Most patients resume light activity within a few days.
- Pain improvement typically begins within 4 to 8 weeks.
- Full biological remodeling continues for several months.
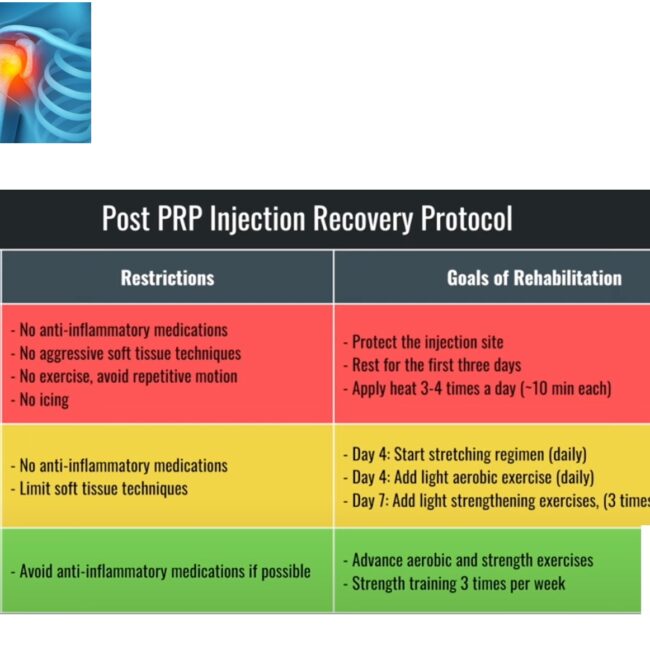
- PRP or physical therapy may be used alongside stem cell therapy to optimize outcomes.
🧠 The Future of Shoulder Regenerative Medicine
The field is evolving rapidly.
Future innovations include:
- Exosome therapy to enhance paracrine effects.
- Gene-edited MSCs for more targeted healing.
- Tissue engineering & scaffolds for complex tendon reconstruction.
- AI-driven protocols for personalized biologic treatment plans.
- Futuristic concept art or schematic of biologic tendon repair.
- ALT text: “Future vision of biologic and scaffold-assisted tendon regeneration.”
📚 References
- Jo CH et al. Intradermal injection of autologous adipose-derived MSCs for rotator cuff disease. Stem Cells. 2018;36:1441–1450.
- Hurd J et al. Safety and efficacy of adipose-derived regenerative cells for partial rotator cuff tears. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15:122.
- Caplan AI. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Time to Change the Name! Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017.
- O’Driscoll SW. Tendon healing and biologic augmentation. JSES.
If you’re suffering from shoulder pain, tendon injury, or early osteoarthritis, regenerative stem cell therapy may help you avoid surgery and restore shoulder function.