Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Shoulder impingement syndrome is one of the most frequent causes of shoulder pain, particularly in people who perform repetitive overhead movements. It may begin with mild discomfort during everyday tasks, but without the right approach, it can gradually limit mobility and affect quality of life.
This condition is common across all age groups, especially among athletes, gym enthusiasts, and professionals with active upper-body use. With the right knowledge and support, shoulder impingement can be managed effectively. This article explains the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options and simple strategies for prevention and recovery.
Why is Shoulder Impingement Syndrome Relevant in Dubai?
Dubai’s lifestyle promotes fitness, productivity and performance. From desk jobs and handheld device use to recreational sports and high-intensity workouts, shoulder strain is a growing concern across all age groups in the city.
Many residents maintain busy professional lives while also participating in sports or gym sessions in the evenings. Activities such as swimming, tennis, paddleboarding, and weightlifting are especially common in Dubai, and these often involve repetitive overhead movements. Without proper technique, the risk of shoulder impingement increases.
Understanding Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
Shoulder impingement syndrome occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff or the bursa in the shoulder become compressed within a narrow space between the top of the shoulder blade (the acromion) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone).
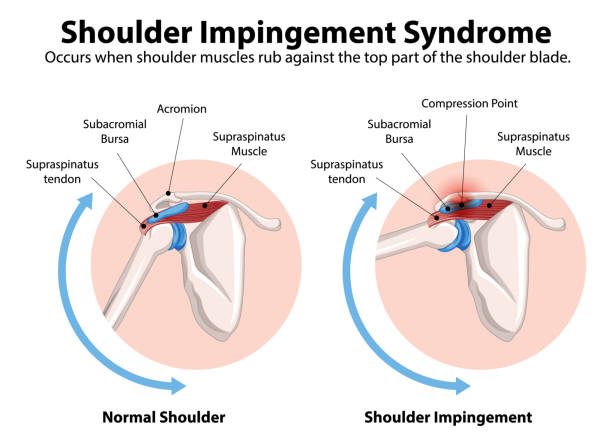
Each time the arm is lifted overhead, this space naturally becomes smaller. If the joint mechanics are not well balanced or the soft tissues are already inflamed, the tendons can become irritated and painful. If left untreated, the condition can progress, leading to chronic inflammation, tendon degeneration, or even rotator cuff tears.
Common Causes of Shoulder Impingement
Understanding the causes of shoulder impingement can help prevent the condition and guide treatment. The most common contributing factors include:
Repetitive Overhead Use
Frequent overhead activity is a major cause. Athletes, weightlifters, swimmers, painters, and individuals who work with their arms elevated are at higher risk.
Poor Posture
Slouched posture, rounded shoulders, or prolonged forward head positioning reduce the subacromial space, increasing friction and pressure on the tendons.
Muscle Imbalance
Weak or tight muscles around the shoulder and upper back can lead to altered joint movement. This places stress on the rotator cuff and the shoulder blade muscles.
Bone Spurs
Over time, small bony growths may form under the acromion, further reducing space and increasing the risk of impingement.
Previous Injuries
Shoulder dislocations, fractures, or past rotator cuff injuries can affect the alignment and function of the joint, leading to impingement symptoms.
Recognising the Symptoms of Shoulder Impingement
Early signs of shoulder impingement syndrome are often mistaken for general muscle strain. However, persistent or worsening symptoms should not be ignored. Key symptoms of shoulder impingement include:
- Pain on the top or outside of the shoulder
- Pain during lifting, reaching, or throwing
- Discomfort when reaching behind the back or overhead
- Pain that worsens at night, especially when lying on the affected side
- Weakness in the arm
- Limited range of motion
Symptoms often build gradually and can worsen without proper care.
How Shoulder Impingement Is Diagnosed
A thorough clinical evaluation is the first step in diagnosing shoulder impingement. The doctor will assess posture, range of motion, strength, and pain triggers. A detailed history is also important to identify any contributing habits or past injuries.
Diagnostic Tests May Include:
- X-rays to rule out structural problems such as arthritis or bone spurs
- Ultrasound or MRI to detect inflammation, tendon tears, or fluid in the joint
- Physical movement tests, such as the Neer or Hawkins tests, which reproduce symptoms to confirm impingement
Early diagnosis can help avoid long-term complications and improve recovery outcomes.
Treatment for Shoulder Impingement
Most cases of shoulder impingement syndrome can be treated successfully without surgery. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation, restoring proper shoulder mechanics, and strengthening the surrounding muscles.
Rest and Activity Modification
Avoiding painful movements and overhead lifting helps reduce inflammation and prevent further damage.
Ice Therapy
Applying an ice pack for 15 to 20 minutes two to three times a day can help manage swelling and discomfort.
Medications
Anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed for short-term relief. These should be taken under medical supervision.
Physiotherapy
Rehabilitation guided by a physiotherapist is often the cornerstone of recovery. A structured programme focuses on improving posture, joint control, and muscle strength. Individualised exercises for shoulder impingement can restore mobility and prevent recurrence.
Corticosteroid Injections
In more stubborn cases, an injection into the subacromial space may provide temporary pain relief and allow physiotherapy to continue more effectively.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is rarely needed. However, if symptoms persist despite several months of conservative care, arthroscopic surgery may be considered to remove bony spurs and increase space in the joint.
Exercises for Shoulder Impingement
A physiotherapist can design a specific exercise routine based on the stage of recovery. Below are commonly prescribed exercises for shoulder impingement:
Pendulum Swings
Gently swing the arm while leaning forward to encourage movement without stress.
Wall Slides
With the back against a wall, slowly raise the arms in a controlled motion to improve coordination.
Resistance Band Rotations
Strengthen the rotator cuff by rotating the arm outward against a light resistance band.
Shoulder Blade Squeezes
Retract and hold the shoulder blades together to improve posture and upper back strength.
Sleeper Stretch
Stretches the back of the shoulder to relieve tightness and improve range.
Each exercise should be performed slowly and without pain. It is important to start under supervision and follow progressions as advised.
How to Prevent Shoulder Impingement
After recovery, prevention is key. The following strategies help reduce the risk of recurrence:
- Maintain upright posture during work and exercise
- Include regular warm-up and shoulder activation before workouts
- Avoid repetitive overhead activities or take regular breaks
- Strengthen the rotator cuff and upper back muscles
- Use proper technique during lifting or sports movements
- Listen to the body and seek guidance early if discomfort returns
A few small adjustments in posture and routine can make a big difference in long-term shoulder health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can shoulder impingement go away on its own?
Mild cases may improve with rest and activity changes. However, persistent symptoms should be evaluated to avoid worsening.
How long does recovery take?
Most people recover within six to twelve weeks with proper treatment. Chronic cases may take longer.
Is it safe to exercise with shoulder impingement?
Yes, but exercises should be specific and guided by a physiotherapist. Painful movements should be avoided.
Is shoulder impingement the same as a rotator cuff tear?
No. Impingement involves irritation and compression, whereas a tear refers to actual damage to the tendon.
When should medical help be sought?
If pain lasts more than two weeks, worsens, or affects sleep and daily activities, a medical consultation is strongly recommended.
A Note from the Specialist
Shoulder impingement is a condition that can be managed very effectively with early intervention and the right care. Ignoring persistent shoulder pain or delaying treatment often leads to longer recovery times and increased risk of tendon damage. Individuals with active lifestyles, poor posture, or previous shoulder injuries should pay close attention to symptoms and seek expert advice when needed.
Conclusion
For accurate diagnosis and expert management of shoulder impingement syndrome, patients in Dubai can consult Dr. Marouane, Consultant Orthopaedic Shoulder Surgeon. With over 20 years of specialised experience, he offers comprehensive care and advanced treatment options tailored to individual needs.